Introduction to Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are a popular investment vehicle that pools money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities, such as stocks, bonds, and other assets. Managed by professional fund managers, mutual funds offer individual investors access to diversified and professionally managed portfolios, which can help reduce investment risk.
What is a Mutual Fund?
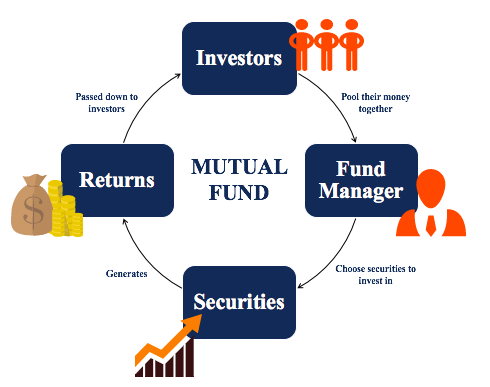
A mutual fund is an investment fund that collects money from multiple investors to purchase a portfolio of assets. These funds are managed by professional fund managers who allocate the fund’s investments with the aim of achieving the fund’s investment objectives.
Types of Mutual Funds
- Equity Funds
- These funds primarily invest in stocks and aim for capital growth. They can be further categorized into large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap funds based on the market capitalization of the companies they invest in.
- Debt Funds
- Debt funds invest in fixed-income securities like bonds, government securities, and money market instruments. They are suitable for investors looking for stable income with lower risk.
- Hybrid Funds
- Hybrid funds invest in a mix of equity and debt instruments, providing a balance of growth and income. They can be balanced funds, aggressive hybrid funds, or conservative hybrid funds depending on their asset allocation.
- Index Funds
- Index funds track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500 or Nifty 50. They aim to replicate the performance of the index and typically have lower expense ratios due to passive management.
- Sector Funds
- Sector funds focus on specific sectors of the economy, such as technology, healthcare, or finance. They carry higher risk as they are concentrated in a particular industry.
- Tax-Saving Funds (ELSS)
- Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) are mutual funds that offer tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act in India. They have a lock-in period of three years.
Benefits of Investing in Mutual Funds

How Mutual Funds Work
When you invest in a mutual fund, you buy shares of the fund. Each share represents a portion of the holdings of the fund. The value of these shares is called the Net Asset Value (NAV), which fluctuates based on the performance of the underlying assets in the fund’s portfolio.
Types of Mutual Funds
- Equity Funds
- These funds primarily invest in stocks and aim for capital growth. They can be further categorized into large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap funds based on the market capitalization of the companies they invest in.
- Debt Funds
- Debt funds invest in fixed-income securities like bonds, government securities, and money market instruments. They are suitable for investors looking for stable income with lower risk.
- Hybrid Funds
- Hybrid funds invest in a mix of equity and debt instruments, providing a balance of growth and income. They can be balanced funds, aggressive hybrid funds, or conservative hybrid funds depending on their asset allocation.
- Index Funds
- Index funds track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500 or Nifty 50. They aim to replicate the performance of the index and typically have lower expense ratios due to passive management.
- Sector Funds
- Sector funds focus on specific sectors of the economy, such as technology, healthcare, or finance. They carry higher risk as they are concentrated in a particular industry.
- Tax-Saving Funds (ELSS)
- Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) are mutual funds that offer tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act in India. They have a lock-in period of three years.
Benefits of Investing in Mutual Funds
- Diversification
- Mutual funds invest in a wide range of securities, reducing the risk associated with individual investments.
- Professional Management
- Experienced fund managers handle the investment decisions, aiming to maximize returns for the investors.
- Liquidity
- Mutual fund units can be bought or sold on any business day, providing flexibility and liquidity to investors.
- Affordability
- Investors can start with a small amount, making mutual funds accessible to a broad range of investors.
- Transparency
- Mutual funds provide regular updates on the performance of the fund and the value of the investment.
How to Invest in Mutual Funds
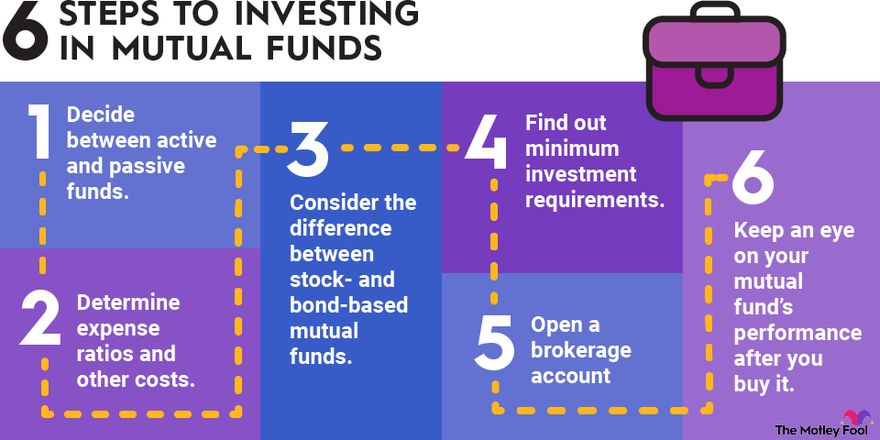
- Define Your Investment Goals
- Determine your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon before choosing a mutual fund.
- Choose the Right Type of Fund
- Based on your goals and risk profile, select the appropriate type of mutual fund (equity, debt, hybrid, etc.).
- Research and Compare Funds
- Look at the past performance, expense ratio, fund manager’s track record, and other factors to compare different mutual funds.
- Open an Account
- You can invest in mutual funds through a mutual fund company, a financial advisor, or an online investment platform. You will need to complete the KYC (Know Your Customer) process.
- Invest Regularly
- Consider starting a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) to invest a fixed amount regularly, taking advantage of rupee cost averaging.
- Monitor Your Investment
- Regularly review the performance of your mutual fund investments and make adjustments as needed to stay aligned with your financial goals.
Systematic Investment Plan (SIP)
What is SIP?
A Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) allows investors to invest a fixed amount regularly (monthly, quarterly, etc.) in a mutual fund. SIPs help inculcate a disciplined investment habit and reduce the impact of market volatility through rupee-cost averaging.

Benefits of SIP
- Disciplined Savings: Encourages regular investing.
- Rupee-Cost Averaging: Buys more units when prices are low and fewer units when prices are high.
- Flexibility: Can start with a small amount and increase over time.
- Compounding: Benefits from the power of compounding over the long term.
How to Start SIP
- Choose a Mutual Fund: Select a fund that aligns with your financial goals.
- Set Up SIP: Decide the amount and frequency of investment.
- Automate Investments: Link your bank account for automatic transfers.
Lump Sum Investment
What is Lump Sum Investment?
A lump sum investment involves investing a large amount of money in a mutual fund at once. This method can be beneficial when the market is undervalued or if you have a substantial amount to invest.

Benefits of Lump Sum Investment
- Potential for Higher Returns: Can capitalize on market opportunities.
- Simple and Convenient: One-time investment without regular follow-ups.
- Suitable for Large Amounts: Ideal for investors with a substantial corpus.
How to Make Lump Sum Investments
- Research: Analyze the market and select the right mutual fund.
- Invest: Invest the entire amount in the chosen fund.
- Monitor: Keep track of the fund’s performance and market conditions.
Mutual Fund Performance and Risk
While mutual funds offer the potential for higher returns, they also come with certain risks, such as market risk, credit risk, and interest rate risk. It’s important to understand these risks and diversify your investments accordingly. Reviewing the fund’s historical performance, investment strategy, and risk factors can help you make informed decisions.

Tax Implications of Mutual Funds
Equity Funds
- Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG): Taxed at 15% if held for less than a year.
- Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG): Taxed at 10% for gains exceeding INR 1 lakh if held for more than a year.
Debt Funds
- Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG): Taxed as per the investor’s income slab if held for less than three years.
- Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG): Taxed at 20% with indexation benefits if held for more than three years.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Lack of Research: Investing without understanding the fund.
- Ignoring Costs: Not considering expense ratios and other fees.
- Chasing Returns: Investing based on past performance without considering future potential.
- Overlooking Diversification: Investing in similar funds and increasing risk.
Conclusion
Mutual funds offer a versatile and accessible way for investors to diversify their portfolios and achieve their financial goals. Whether you choose to invest through SIPs or lump sum, understanding the basics and doing thorough research can help you make informed decisions and maximize your returns.
“Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Mutual Fund”
What is a Mutual Fund?
A mutual fund is an investment vehicle that pools money from various investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. Managed by professional fund managers, mutual funds aim to generate returns for investors based on the fund’s objectives. They offer an accessible way for individuals to invest in the stock market without needing extensive knowledge or significant capital.
How does a mutual fund work?
Investors buy units of a mutual fund, and the collected money is used to purchase a diversified portfolio of securities. The fund’s value is determined by the performance of these securities, and investors earn returns based on the fund’s overall performance.
What are the different types of mutual funds available in India?
There are various types of mutual funds, including:
Equity Funds: Invest primarily in stocks.
Debt Funds: Invest in bonds and other debt instruments.
Hybrid Funds: Combine both equity and debt investments.
Index Funds: Track a specific market index.
Liquid Funds: Invest in short-term money market instruments.
What is SIP in mutual funds?
A Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) is a method of investing in mutual funds. It allows investors to invest a fixed amount regularly (e.g., monthly) in a mutual fund scheme, making it easier to build wealth over time through disciplined investing.
What is the difference between SIP and lump sum investment?
In a SIP, investors invest a fixed amount at regular intervals, while in a lump sum investment, the entire amount is invested at once. SIPs help in averaging the purchase cost and mitigate the impact of market volatility, while lump sum investments can benefit from investing in a favorable market condition.
How can I start investing in mutual funds in India?
To start investing in mutual funds, you need to:
Complete KYC (Know Your Customer) formalities.
Choose a suitable mutual fund scheme based on your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Decide between SIP or lump sum investment.
Invest through a mutual fund distributor, advisor, or directly through the AMC’s website.
What are the tax implications of investing in mutual funds in India?
The tax implications vary depending on the type of mutual fund and the holding period. For example:
Equity Funds: Short-term capital gains (holding period less than one year) are taxed at 15%, while long-term capital gains (holding period more than one year) exceeding ₹1 lakh are taxed at 10%.
Debt Funds: Short-term capital gains are added to the investor’s income and taxed as per their tax slab, while long-term capital gains are taxed at 20% with indexation benefits.
What is the NAV of a mutual fund?
The Net Asset Value (NAV) represents the per-unit value of a mutual fund. It is calculated by dividing the total value of the fund’s assets (minus liabilities) by the number of units outstanding. NAV changes daily based on the market value of the fund’s holdings.
Can I withdraw my money from a mutual fund at any time?
Yes, you can withdraw your investment from an open-ended mutual fund scheme at any time. However, some funds may have an exit load if you withdraw before a specified period. Close-ended funds can only be redeemed at maturity or traded on the stock exchange.
How do I choose the right mutual fund?
Choosing the right mutual fund depends on factors such as your investment goals, risk tolerance, time horizon, and the fund’s past performance. It’s advisable to consult with a financial advisor or use online tools and resources to compare different mutual funds.