The stock market serves as a barometer for the economy and reflects a nation’s financial health. In India, the stock market plays a significant role, not just in shaping the domestic economy but also in influencing global activities. With India emerging as one of the world’s fastest-growing economies, its stock market’s performance has a ripple effect on various aspects of the global financial system.
In this blog, we will explore how the Indian stock market affects global activities, including examples that highlight its impact.
1. Global Investment Flows
India’s stock market attracts a substantial amount of foreign investment, particularly from institutional investors. When the Indian market performs well, it draws in capital from around the world. Conversely, poor performance can lead to capital outflows, affecting global liquidity and investment strategies.
Example:
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): A strong performance in sectors like IT, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing can attract foreign investors, leading to increased FDI. This has a direct impact on the countries where these investments originate, influencing their economic activities.
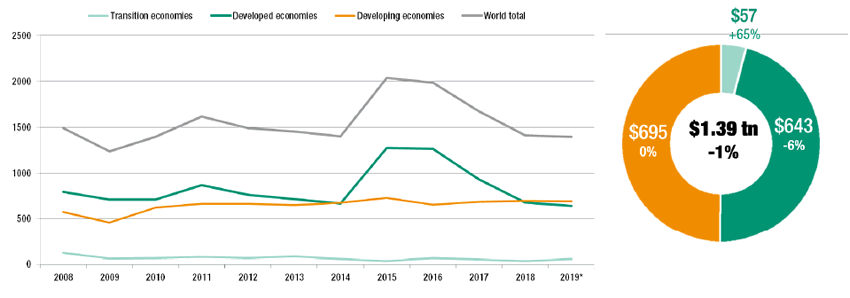
2. Impact on Global Markets
The performance of India’s stock market is closely watched by global investors, as it is a key indicator of the country’s economic strength. A significant movement in the Indian market can lead to reactions in other major stock markets, particularly in emerging markets.
Example:
- Correlation with U.S. and European Markets: If the Indian market experiences a sharp decline due to political instability or economic concerns, it may cause a ripple effect in global markets. Investors might pull out from other emerging markets as well, leading to a broader sell-off.
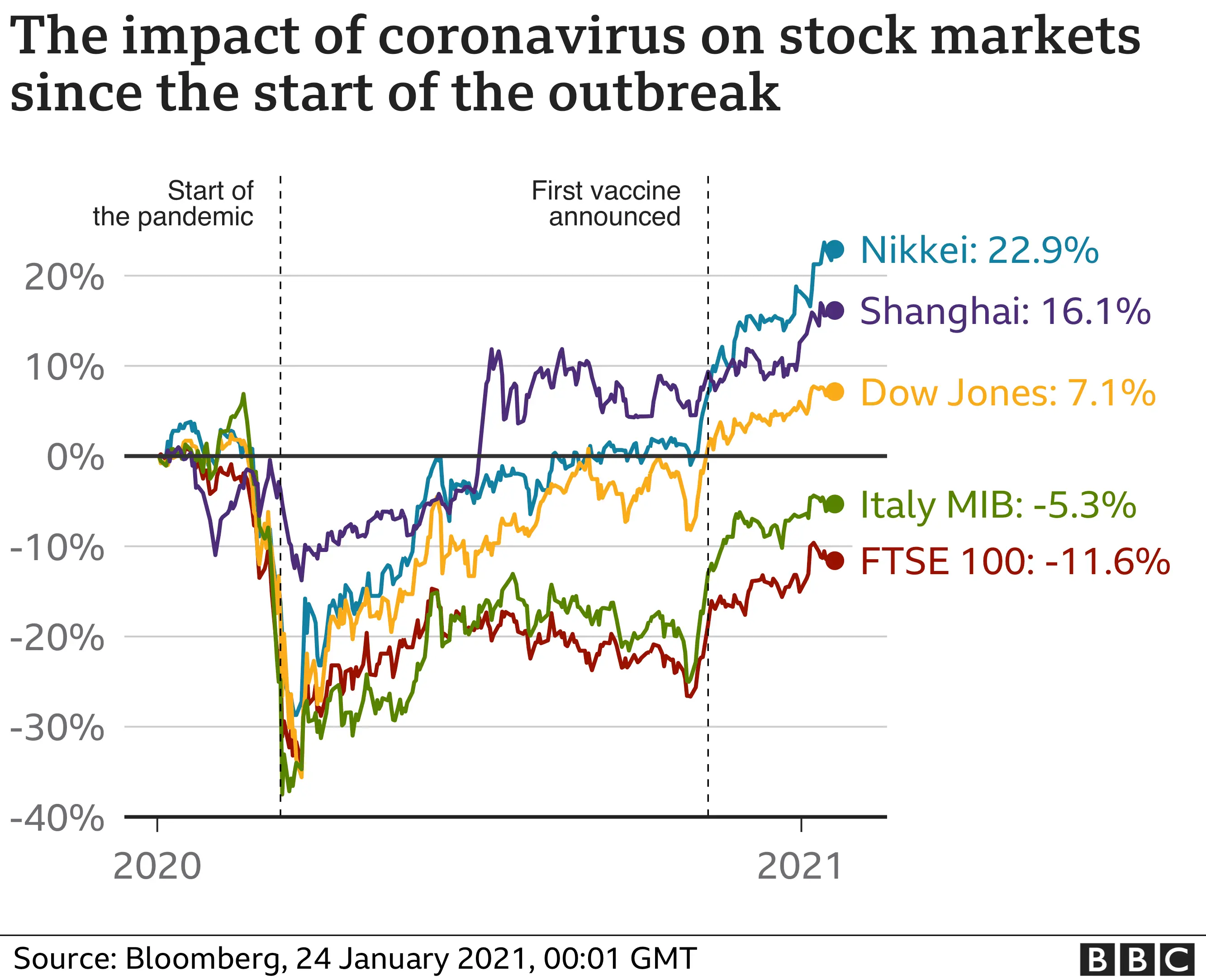
3. Influence on Commodity Prices
India is one of the largest consumers of commodities like oil, gold, and agricultural products. The stock market’s performance, particularly in sectors like energy and manufacturing, can influence global commodity prices. A robust market can drive demand for commodities, pushing up prices globally.
Example:
- Crude Oil: India’s demand for oil has a direct impact on global oil prices. When the stock market reflects growth in sectors like manufacturing and transportation, it signals increased demand for oil, which can lead to higher global prices.

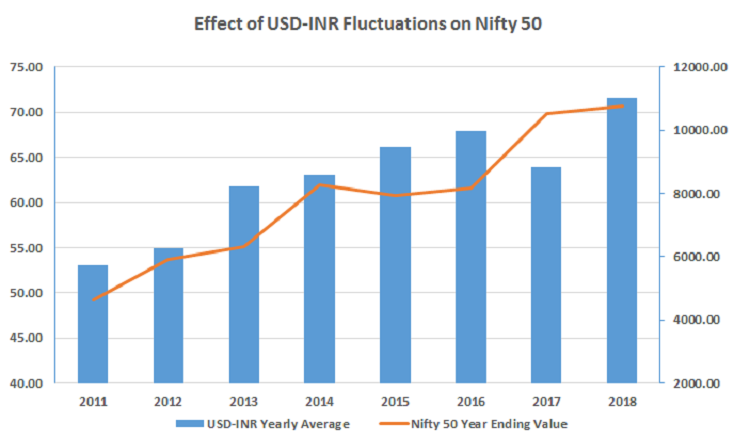
4. Currency Exchange Rates
The Indian stock market also plays a role in determining the value of the Indian Rupee (INR) against other major currencies. Fluctuations in the stock market can lead to changes in currency exchange rates, which in turn affect global trade and investments.
Example:
- INR vs. USD: If the Indian stock market witnesses a surge due to positive economic data, it may lead to an appreciation of the INR. This can impact global trade dynamics, particularly for countries that have significant trade relations with India.
5. Technological Advancements and Globalization
India’s stock market is home to many technology-driven companies, particularly in the IT and telecom sectors. The performance of these companies can influence global technological trends and collaborations, as well as the outsourcing industry.
Example:
- IT Sector: Companies like Infosys, TCS, and Wipro are global leaders in IT services. Their stock performance reflects their business growth, which has a direct impact on global clients and partners, especially in the U.S. and Europe.

“Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About How the Stock Market in India Affects World Activities”
How does the Indian stock market influence global economic trends?
The Indian stock market is interconnected with global markets through trade, investments, and economic policies. Changes in India’s stock market, driven by domestic or international events, can set the tone for global economic trends. For example, a boom in the Indian technology sector can attract foreign investments, boosting the global tech industry. Conversely, a downturn in Indian markets can trigger caution among global investors, affecting markets worldwide.
Example: During the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, when the Indian stock market faced a significant downturn, it led to a ripple effect in other emerging markets, causing a broader global market sell-off.
What role does foreign investment play in linking the Indian stock market to world activities?
Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) play a crucial role in linking the Indian stock market to global financial activities. When foreign investors invest heavily in Indian equities, they contribute to global capital flows. Conversely, when FIIs pull out of the Indian market due to economic or political uncertainties, it can lead to volatility in other markets, particularly in regions with similar investment profiles.
Example: In 2022, when foreign investors started withdrawing funds from Indian markets due to global economic uncertainties, it caused a domino effect, leading to a sell-off in other emerging markets as well.
How do global events impact the Indian stock market, and vice versa?
Global events, such as geopolitical tensions, changes in commodity prices, or economic policies in major economies, can have a direct impact on the Indian stock market. Similarly, significant developments in India, such as changes in government policies, corporate earnings, or major market movements, can influence global markets.
Example: The U.S.-China trade war had a significant impact on the Indian stock market, leading to volatility in sectors like technology and manufacturing. On the other hand, the Indian government’s decision to ban high-denomination currency notes in 2016 (demonetization) caught the attention of global markets, affecting foreign investment flows into India.
How does India’s economic growth impact global markets?
India’s economic growth is closely watched by global investors and institutions. Strong economic growth in India often leads to increased foreign investments, boosting global capital markets. Moreover, India’s growing middle class and consumer market are vital for multinational companies, making India’s economic performance a key indicator for global business strategies.
Example: India’s rapid economic growth between 2014-2019 attracted substantial foreign investments, particularly in the technology and e-commerce sectors. This led to global companies like Amazon and Walmart increasing their investments in India, impacting their global operations and stock prices.
How do Indian companies listed on global exchanges influence world markets?
Several Indian companies are listed on global exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or NASDAQ. These companies, often from sectors like technology, pharmaceuticals, and energy, play a vital role in global trade and investment. Their performance on international exchanges reflects not only the health of these companies but also the broader Indian economy, influencing global market sentiments.
Example: Infosys, an Indian IT giant, is listed on NASDAQ. Its quarterly earnings reports and business outlook often influence global tech stocks, reflecting the interdependence between Indian companies and world markets.
How does the Indian stock market respond to changes in global commodity prices?
India is a major importer of commodities like oil and gold. Changes in global commodity prices can directly affect the Indian stock market. For example, a rise in oil prices can lead to increased inflation and a weakening of the Indian rupee, affecting sectors like transportation, manufacturing, and energy, which in turn impacts global markets.
Example: In 2022, the surge in global oil prices due to geopolitical tensions led to a decline in Indian stocks, particularly in sectors dependent on fuel. This, in turn, affected global markets, especially in countries that have strong trade ties with India.
What is the impact of Indian government policies on global markets?
Indian government policies, particularly those related to taxation, trade, and foreign investment, can have a significant impact on global markets. Favorable policies can attract foreign investments, while restrictive policies may deter them. The global market often reacts to announcements of major policy changes in India.
Example: The implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India in 2017 was closely monitored by global investors. The tax reform aimed at simplifying the tax structure and boosting economic growth attracted foreign investments, positively impacting global markets.
How do Indian stock market indices correlate with global indices?
Indian stock market indices like the Sensex and Nifty are often correlated with global indices like the S&P 500 or FTSE 100. A strong correlation means that a rise or fall in Indian indices can influence global indices and vice versa. This correlation is often driven by global economic conditions, investor sentiment, and capital flows.
Example: During the global financial crisis of 2008, Indian indices like the Sensex saw a significant decline, mirroring the fall in global indices like the Dow Jones Industrial Average. This correlation highlighted the interconnectedness of global markets.
How do Indian exports and imports affect global trade?
India is a major player in global trade, with its exports and imports having a direct impact on global supply chains. Changes in the Indian stock market, reflecting the health of export-oriented industries like textiles, pharmaceuticals, and IT, can influence global trade dynamics.
Example: The disruption of pharmaceutical exports from India during the COVID-19 pandemic led to a shortage of generic drugs in several countries, affecting global healthcare markets.
How does investor sentiment in India affect global investor behavior?
Investor sentiment in India, driven by economic conditions, corporate performance, and political stability, can influence global investor behavior. A positive outlook in India can attract foreign investments, while negative sentiment can lead to a pullback from global investors, impacting other emerging markets.
Example: In 2020, despite the global economic downturn, positive investor sentiment in India due to strong corporate earnings in the tech sector led to an influx of foreign investments. This, in turn, boosted investor confidence in other emerging markets.